題目敘述
Given the root of a binary tree, return all duplicate subtrees.
For each kind of duplicate subtrees, you only need to return the root node of any one of them.
Two trees are duplicate if they have the same structure with the same node values.
Example 1.
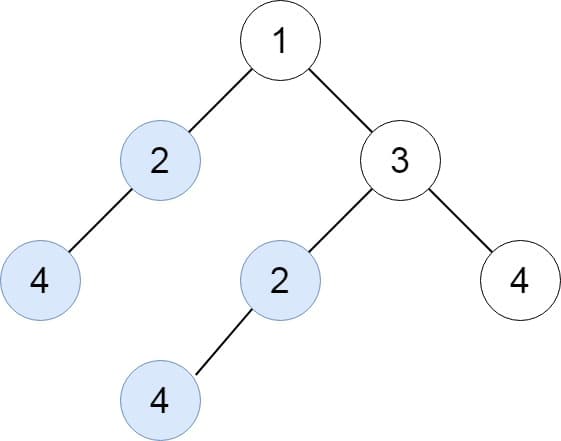
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,null,2,4,null,null,4]
Output: [[2,4],[4]]
Example 2.
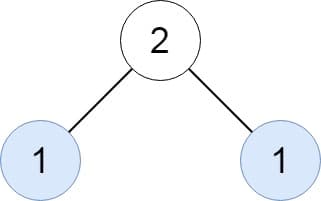
Input: root = [2,1,1]
Output: [[1]]
Example 3.
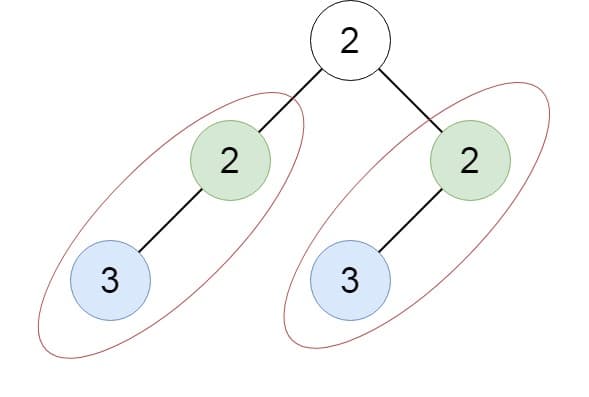
Input: root = [2,2,2,3,null,3,null]
Output: [[2,3],[3]]
限制:
The number of the nodes in the tree will be in the range [1, 5000]-200 <= Node.val <= 200
解題思路:
所有這種 find duplicate 的問題其實最重要的都是要思考如何紀錄已經出現過的元素。
在這題因為要找的是的相同的 Subtree,而在一般來說 Tree 只會給一個 root,並沒有辦法快速看出整個 Tree 的全貌,所以我們就要思考如何整個 Tree 都存起來。
當然我們可以選擇直接把整個 Tree 變成一個 string 來存,以下面這張圖為例:

在這邊以 1 為 root,我們把每個 root 的 children 都用括號的形式放在左右兩邊就可以把他存成 ((4)2())1((((4)2())2())3(4)) 的形式,但這樣的形式在我們裡用 post order traverse 整顆 tree 的時候每個 subtree 都會最差都可能有 n 個 node,因此會需要花費額外的時間(O(n))來成這個 String。
所以在這邊更好的方式其實是給每一個 subtree 一個屬於他的 id,之後在做 post order traverse 的時候,我們把 string 變成 leftSubTreeId + ',' + node.value + ',' + rightSubTreeId,這樣就只會需要 3 個數字相加所以就可以節省很多的時間。
另外設立一個 count 的 Hash Map 來存每個 subtree 出現的次數,在出現第 2 次的時候就把他加入到 result,最後回傳 result 就好啦!
解題步驟:
- 宣告 tripletIdMap, counts 兩個 Hash Map 和一個 List
result - 在 traverse 裡面:
- 對 node.left 做 traverse 來獲得左 subtree 的 id
- 對 node.right 做 traverse 來獲得右 subtree 的 id
- 把上面兩個 id 和 node.value 組成 string
triplet - 如果 triplet 不在 tripletIdMap 裡面的話,就把它存進去並且 id 為
tiprletIdMap.size() + 1 - 反之則是從 tripletIdMap 裡面拿到 id 之後去 counts 裡面把那個 id 的 count + 1
- 如果該 triplet 的
count == 2的話就把 node 加到 result 裡面。 - return id 讓遞迴的上層可以拿到 id 並且組成他的 triplet。
- 在整個 traverse 結束之後,我們就會得到結果了!
Java 解法
class Solution {
private List<TreeNode> result;
private HashMap<String, Integer> tripletIdMap;
private HashMap<Integer, Integer> counts;
public List<TreeNode> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode root) {
this.result = new ArrayList<>();
this.tripletIdMap = new HashMap<>();
this.counts = new HashMap<>();
traverse(root);
return this.result;
}
private int traverse(TreeNode node) {
if (node == null) return 0;
String triplet = traverse(node.left) + "," + node.val + "," + traverse(node.right);
int id = 0;
if (!this.tripletIdMap.containsKey(triplet)) {
id = this.tripletIdMap.size() + 1;
this.tripletIdMap.put(triplet, id);
this.counts.put(id, 1);
} else {
id = this.tripletIdMap.get(triplet);
this.counts.put(id, this.counts.get(id) + 1);
}
if (this.counts.get(id) == 2) this.result.add(node);
return id;
}
}
Complexity
- Time Complexity: O(n);
- Space Complexity: O(n);